Anxiety is an emotion that tends to seek out confirmation. It is a normal reaction to stress. It can alert us to dangers. It is a type of fear that you experience when you have thoughts of threat or something going wrong in the future, rather than present. While at times this can be validating, it can also intensify the emotion, leaving you feeling helpless and overwhelmed. It is part of the body’s natural reaction to stress, so it can be helpful at times, making you more alert and ready for action.

Experiencing occasional anxiety occasionally is a normal part of life. However, those people with regular anxiety disorders have intensively, more excessive, and persistent worry and fear in daily situations. Normally, anxiety disorders relate to repeated stages of unexpected feelings about anxiety and fear or in a few minutes (panic attacks). These feelings of anxiety and panic disturb daily activities and are difficult to control outside the actual danger and survive for a long time. You can avoid places or situations to prevent these feelings. Symptoms if Anxiety mostly starts during childhood or adolescence and continue to adults. According to the World Health Organization, it is estimated that 28% of the world’s population of the world have an anxiety disorder.
Examples of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder (social phobia), specific phobias, and separation anxiety disorder. You can have more than one anxiety disorder. Sometimes anxiety results from a medical condition that needs treatment.
Many people with anxiety experience one or more symptoms and can experience depression as well. Symptoms of anxiety are not likely to subside overtime; they begin to dominate life if left untreated.
Types of anxiety disorders:
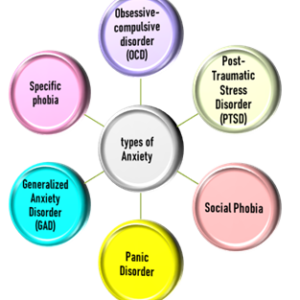 There are several types of anxiety disorders that exists. And below are a few discussed:
There are several types of anxiety disorders that exists. And below are a few discussed:
-
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
Most people may feel anxious and worried, especially when faced with stressful situations which are to some extent normal, such as going to a job interview, participating in a game, or preparing for an event. This anxiety helps you feel focused, getting things done quickly, and performing at your best.
However, people with generalized anxiety disorder feel extremely anxious and worried in most cases, not just in certain stressful situations. These worries are severe and lasting and interfere with everyday life. Their concerns are not only related to one problem, but to many aspects of their daily life, including work, health, family, and financial problems. Even the smallest of chores or delays in appointments can become a focal point of anxiety and lead to excessive worry or a feeling that something terrible is about to happen.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
-
- Specific phobia:
When people imagine danger or react unreasonably exaggeratedly to things, activities or situations (fear stimuli), they are called specific phobia. Their feelings of panic, fear, or fear are not completely out of balance with the actual threat. Sometimes the mere thought of the phobia stimuli or the sight of images and videos on screens trigger a reaction. This type of overreaction can indicate a specific phobia.
Specific phobias are aware that their concerns are exaggerated or unreasonable, but feel they have no control over whether the anxiety response is automatic. Certain phobias are often associated with panic attacks, during which you experience overwhelming bodily sensations such as heart palpitations, choking, vomiting, fainting, dizziness, chest pain, hot or cold flushes, and sweating.
- Specific phobia:
-
-
- Social Phobia:
feeling anxious in social situations where we might come under the attention of others, be it strangers or people we are familiar with. Attending an official event, giving a presentation to a colleague at work or even being called to answer questions in class can provoke tension and anxiety during the preparation and event. However, we call it social phobia when doing such activities in front of others or at social gatherings cause serious anxiety. People with social phobia are afraid of being criticized, ridiculed, and humiliated in front of others, even in the most everyday situations.
Social phobia can also be specific. If people are afraid of a particular situation or some situations related to a particular phobia (e.g., be strong at work or with friends). - Panic Disorder: Panic disorder is when panic attacks are recurrent and disabling Fears and worries are two main characteristics of panic disorder. Even in the absence of real danger, affected individuals develop physical reactions, such as nausea, deep breathing, and tremors, as if some threat was imminent. These people also suffer from constant anxiety about when their next panic attack will occur.
- Social Phobia:
-
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD):
OCD is a disorder in which there are repetitive unnecessary thoughts, thoughts and sensations (obsessive-compulsive thoughts) that makes a person feel the urge (compulsion) to do something repeatedly. People with OCD often feel serious shame about the need to carry out these coercions. This shame can exacerbate the problem and shame, and as a result, the secrets associated with OCD can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment. It can also be a social obstacle, such as children not attending school or adults being trapped in their homes.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD):
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a series of specific reactions that can occur in people who have experienced traumatic events that threaten the lives and safety of themselves and those around them. This can result in a car or other serious accident, physical or sexual assault, war or torture, or a disaster such as a wildfire or flood. As a result, the person experiences intense feelings of fear, helplessness, or fear.
-
Causes of Anxiety Disorders:
Anxiety disorders are another form of mental illness. They do not come from personal weaknesses, defects of character, or problems of upbringing. However, researchers do not know exactly what causes anxiety disorders. They think a combination of factors is playing a role.
- Chemical imbalance: Severe or long-term stress can change the chemical balance that regulates feelings. It can lead to anxiety disorders that are stressed for long periods of time.
- Environmental Factors: Trauma can cause anxiety disorders, especially in people at high risk.
- Heredity: Anxiety disorders tend to have a family history. Like eye color, it can be inherited from either or both parents. Causes of Stress Traumatic events or traumatic events such as the death of a loved one or child abuse can cause this condition.
- Changes in areas of the brain that controls structural stress and anxiety can cause disability.
SYMPTOMS OF ANXIETY
Symptoms of anxiety could be physical, mental, or behavioural.
Physical symptoms:
• Cold or sweaty hands.
• Dry mouth.
• Nausea.
• Shortness of breath.
• Paralysis or tingling in the hands and legs.
• Muscle tension.
• Heart palpitations.
Mental symptoms:
• Nightmare.
• Feeling anxious, panicking
• Uncontrollable, obsessive thoughts.
• Thoughts or flashbacks of recurring traumatic experiences.
Behavioural symptoms:
• Quiet and restless.
• Obsessive behaviour like washing your hands repeatedly.
• problem sleeping.
EFFECTS OF ANXIETY
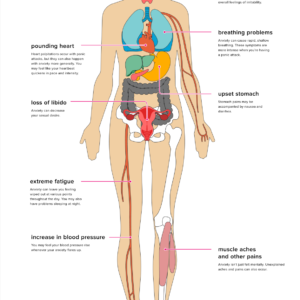
TREATMENT FOR ANXIETY
There are several ways of treating anxiety which include but not limited to:
- Psychotherapy:
Seeing a psychotherapist so you can talk about your anxiety panics is a proven way of treating anxiety. Psychotherapists provide a form of talk therapy to voice out one concerns and speak about issues that trigger or are triggering anxious thoughts. - Medication:
Taking medication such as sedatives and anti-depressants work on the brain to balance its chemistry. It helps to prevent episodes of anxiety. It also wards off the severe symptoms of anxiety disorder.
Natural ways of treating anxiety:
a) It’s essential; to get enough sleep or rest. It helps in keeping the individual calm
b) Another way of treating anxiety is by staying active or exercising.
c) Eating a healthy diet especially one’s rich in omega 3 such as salmon. Chamomile, Turmeric and other foods like yoghurt, green tea and dark chocolate helps in treating anxiety.
d) Avoiding alcohol is another treatment for anxiety
e) An individual who is suffering from anxiety but smokes should quit smoking. This greatly helps in treating anxiety.
f) There is the need to have a support network like friends and family to help one cope with anxiety
g) Stress management techniques such as yoga and meditating are other ways of coping with anxiety.

